How you can stop them from happening.
Like a biological virus mutates – as technology advances so do the complexity of phishing and identity theft schemes. With major services adopting cloud technologies and storing private data online, anyone is vulnerable to hacking.
To make matters worse, hackers continue to come up with some pretty creative ways to profit from stolen information.
Without wasting time, these are the things you should already be doing to avoid being exposed to hackers in the first place:
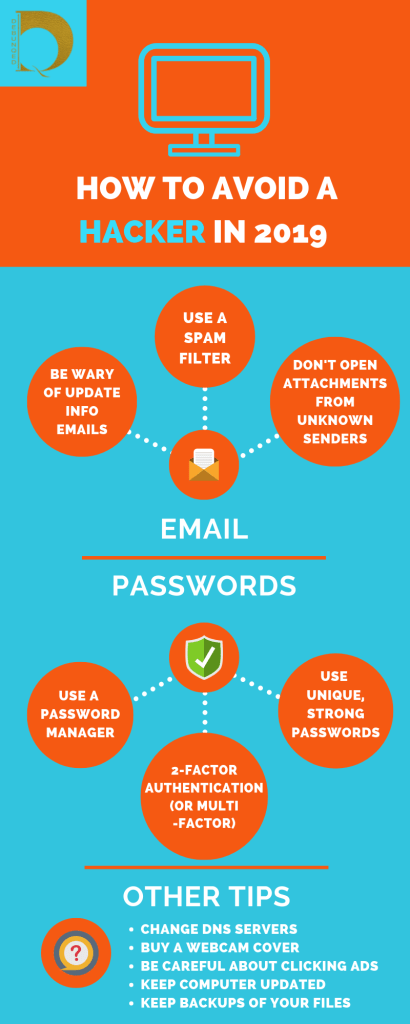
In order to keep these cyber-criminals out of your lives and computers, let’s take a look at some of the actual schemes to watch out for in 2019.
Hacking
We all know what hacking is by now – the term has almost become synonymous with internet security. So a question is: do you love watching movies on Netflix or jamming out to your summer playlist on Spotify? If the answer is yes, then you’re at a pretty high risk of getting hacked.
DynaRisk, a UK cybersecurity firm, recently found that cybercriminals most commonly target these brands, along with adult-oriented sites (you know what we mean) and then, online gaming services.
Identity Theft
A few weeks ago, authorities caught a New York-based gang who had used identity theft to steal over $19 million worth of iPhones. Quartz reported that this operation ran for seven years.
So-called “Top Dogs,” the ring leaders, would organize lower level members of their organization to steal identities and create clone credit and identity cards. Then, affiliates fanned across the nation, signing up for mobile phone plans to acquire iPhones, which were later sold for a profit by the Top Dogs.
Because phone payment plans take the shape of nominal fees over the course of several years, victims often wouldn’t notice the fraud until it was too late. Learn how another scheme dubbed sim port attack works in the diagram below:

Ransomware
Hacking can happen to anyone – including our favorite bands. In early June, a hacker managed to steal the minidisk archive of Thom Yorke, the lead singer of Radiohead. This included previously unreleased demos and audio material from around the time of “OK Computer,” the band’s 1997 worldwide hit album. The hacker then demanded $150,000 on the threat of releasing it.
Holding files for ransom is so common nowadays that it even has its own name: “Ransomware.” Either pay over the ransom or lose your files—or, even worse, have them released onto the unforgiving Internet.
In response, Radiohead released all 18 hours of material on Bandcamp themselves, winning against these ransom hackers.
Most security experts recommend the same route as Radiohead—never pay the ransom, because there’s no guarantee you’ll recover files or prevent their release.
Sextortion
If you think ransomware is bad, there’s an entire subgroup of it aimed to profit off sexual shame. Cheekily named “Sextortion,” some hackers creatively upgraded the classic email phishing scam to scare victims into handing over Bitcoin.

According to Fortune, hackers have already racked up over $900,000 with sextortion. In these phishing emails, the sender claims to have spied on you while you watched porn—and has webcam footage of the salacious deeds. The message then demands a Bitcoin ransom, or else face the social and professional consequences of this lewd video getting sent to all your contacts.
To make the threat even more believable, the sender references a previous password tied to the user’s email account. According to Krebson Security, a sextortion phishing message might look a little like what’s written in the sidebox.
In rare cases, the threats are real—and hackers get their hands on some sexually explicit photos. Recently, American actress Bella Thorne fell victim to sextortion. Last Saturday, she took a similar, albeit more risqué, route as Radiohead, opting to release her nude photographs on Twitter in order to take the power away from her hacker.
Last thoughts
So, what’s the best way to avoid your personal, or, business from costing thousands in virtual currency? Since most of these emails are fake, you can just avoid them with a spam filter. And you should probably buy a webcam cover…just to be safe. When it comes to general browsing- we suggest using a VPN.
There are now more secure anti-hacking tools that use the Blockchain and offer great protection, especially against identity theft. Have a look at our feature on Tokenisation.
Most online services now like mobile banks, offer App-based 2-factor authentication. This should now be regarded as the minimum security for ANY online account or App.
To avoid hacking or phishing scams in general, optimizing your cybersecurity and using online common sense will save you loads of time, trouble and money.


Leave a Reply