What does a small-scale farm-holding, two presidents, some tech companies, and their respective local currencies all have in common?
The answer might be obvious if you have been paying attention to the so-called trade war between China and the US in the news lately.
But why is it of concern and what are the far-reaching implications for the rest of the world?
Active involvement in international trade is a vital sign of your country’s financial health and boosts its Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
GDP measures the value of all goods and services produced in a country. From raw materials (input costs) to value-added (assembly and skilled labour costs) to come up with final goods or services.
And though “domestic” implies that this refers to your country’s internal economy, the contributions can be extended from a services perspective.
This occurs when your country places emphasis on or relies on income from Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) to help boost its economy via its GNP. GNP is a similar measurement but slightly different from GDP as it incorporates.
Importance of trade
Fact is, all our goods and services come from unit price or costs that arise from the initial extraction of raw materials.
These then undergo production leading to the product or service of intrinsic value for both local and international (via exports) consumption.
An ideal situation for your country is to export more than it imports to maintain a positive balance of trade. So basically more money flowing in than out.
The trade surplus is then plowed into your economy via the fiscal budget. It can supplement a shortage of funds raised from domestic taxes.
The opposite, which isn’t always a bad thing, (trade deficit) would have to be managed and nursed like any other loan.
The US has often criticized Germany for exporting a lot (cars, trains, and machinery) but not importing much. This is deemed not being ‘fair’ in trade practice. But trade itself arises from market forces, priorities, and consumer demand.
We all love a BMW, Audi, and Mercedes Benz. So these German-made products will always be in demand compared to US car makes.
Who you chose to trade with gives rise to favourable balance of trade if you are engaged in a trade agreement or a trading bloc.
Why this is also a big deal
The demand for your country’s goods and services will directly impact the strength of its local currency. More trade means more of your currency is required to pay for goods and so its value goes up.
A strong local currency leads to stronger purchasing power for its citizens and residents. Comes in handy when you plan things like holidays, purchase goods online, invest or just send cash abroad as gifts.
So, you can see why a strong Dollar or Euro is always favoured and why sometimes drastic measures are taken to keep it that way.
“A higher demand for your country’s products has a direct positive impact on its currency and exchange rate”
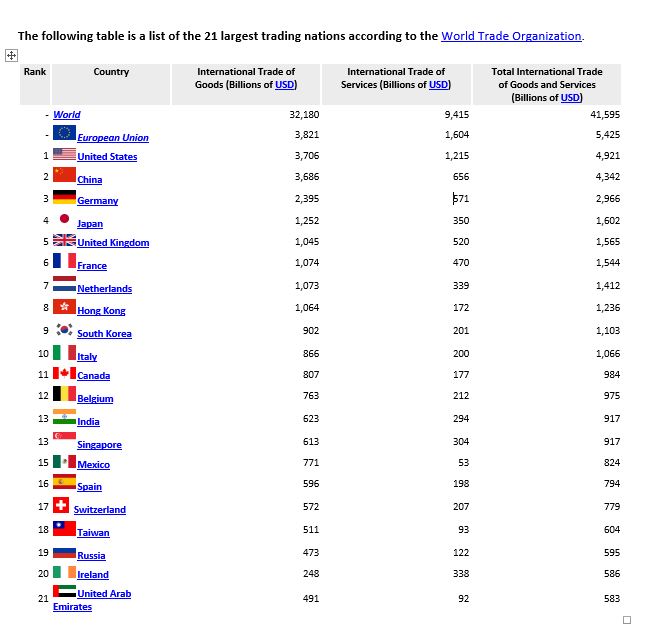
A quick glimpse of the world in terms of the input costs for goods and services gives it a competitive edge when it comes to trade.
- US – intellectual property, services, weaponry.
- Germany – steel and engineering machinery giving rise to high performing automobiles.
- Many African countries – mineral resources such as oil, tobacco cocoa, and precious stones.
- Israel – military intelligence.
- South America – agricultural produce.
- India – IT and customer services.
- China – agriculture, building/(manual) labour, and of late technology.
The beef with China
The technology that China (no.2 on the list) offers the rest of the world is the subject of hot debate. The alleged theft of US intellectual property for tech gadgets and software by China.
This is one of several unfair trade practises and motives for why the US recently decided to start imposing heavier (punitive) tax-like increases on multiple goods imported by China.
These extra costs, referred to in trade terms as import tariffs, have a spill-over effect on the costs of production.
China then reciprocated by hitting the US with tariffs (on agricultural produce) causing the trade war that drives each country to protect its own economy.
The higher input costs naturally, lead to the price of your product going up and reducing its competitive advantage and demand. Higher input costs can also affect your local labour force for the worse too.
Factories, multinational corporations, and industries such as farms (both commercial and subsistence) will have to cut the cost of labour. In worse cases which we have seen, workers are laid-off in a heartbeat to stop or prevent accounting losses.
These factors would have hopefully been taken into consideration by the respective leaders before pulling the tariff triggers. Acting with emotions rather than looking at the far-reaching implications is irresponsible.
Have the talks of the trade war impacted productivity and the global trade economy? So far it’s just the stock markets (securities and commodities) reacting. Only time will tell.