Did you know that there are still more than 700 million people in the world who live in extreme poverty? These people must scrimp, starve, and struggle to survive off less than $1.90 per day.
By 2030, the World Bank estimates that more than 90 percent of those people will be concentrated in Sub-Saharan Africa.
This is perhaps one of the greatest developmental failures of the modern world. Despite the continent’s expansive natural resources and increasing connectivity, foreign actors still feel it’s too risky to heavily invest in their markets.
Blockchain could be the key!
Bitcoin and “Blockchain” were created in the mass wave of distrust in banks after the 2008 financial crisis. Therefore, the technology enables individual, distributed data storage that could become the perfect evidence (trust) base and financial infrastructure for a developing country.
With the right implementation, Blockchain holds the potential to completely revolutionize and revitalize such economies, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa.
So, what is this Blockchain?
Blockchain is essentially a kind of decentralized database that allows you to have a safe, secure way to handle their data without the need for third parties.
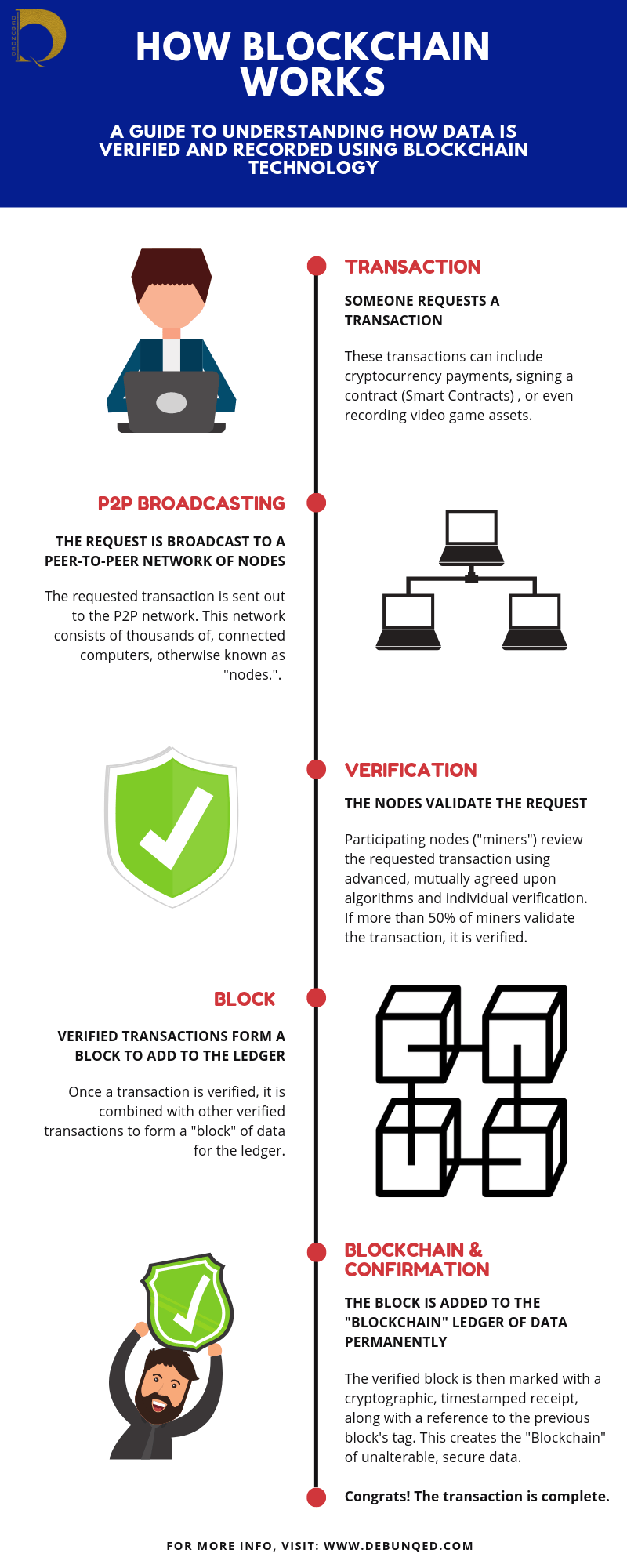
For example, you could with Bitcoin, make or accept payments in real-time without needing a centralized bank.
“[It is] a way for one Internet user to transfer a unique piece of digital property to another Internet user, such that the transfer is guaranteed to be safe and secure, everyone knows that the transfer has taken place, and nobody can challenge the legitimacy of the transfer,” said software entrepreneur Marc Andreessen.
“The consequences of this breakthrough are hard to overstate.”
Historic background
Until the mid-twentieth century, most of Africa was ruled under a colonial system meant to exploit the people and their natural resources for European benefit. Africans, in addition, were rushed into development according to European standards rather than homegrown ones.
The legacy of rapid development, distrust and corruption left behind an economic system failing to recover in the 21st century.
While the World Bank celebrates a decrease in global poverty levels, the number is expected to remain stagnant in Africa. Today’s poorest people are living in places with the least economic growth.
Sadly enough, poverty and lack of investment in many developing countries stem from how they were integrated into the world system.
The land was cut into countries according to European treaties and agreements, rather than by traditional and tribal land divisions. This situation worsened upon the handover of colonial power to so-called “democracies.” Power often shifted to the ethnic groups that former colonizers favoured.
Corruption multiplied in the form of bribes, political persecution, rigged elections, and a massive wealth gap. All of this still affects the wealth distribution and investment potentials of many developing countries.
Of course, this created a lack of trust in banks and government throughout much of Sub-Saharan Africa.
The perfect fit for Africa
During a 2012 study conducted in rural Western Kenya, Stanford University researchers waived the costs of opening basic savings accounts for a number of unbanked individuals.
While 63 percent of the subjects opened an account, only 18 percent of them used the accounts. This was likely due to three factors: a lack of trust in banks, unreliable service and prohibitive withdrawal fees.
Unfortunately, the prevalence of unbanked individuals in the informal sectors scares off foreign investors, who heavily rely on transactional evidence to make investments. Otherwise, pouring money into markets is too risky. That’s where Blockchain comes in.
How would it work?
Blockchain can host an entire evidence base of transactions, loan repayments, and asset titles. The technology is also decentralized and requires individual confirmation, creating an element of trust and transparency beyond traditional banking systems.

According to Victor Olorunfemi, Director of Products for Pan-African tech and crypto-exchange, KuBitX, Blockchain’s major benefits lie in “frictionless P2P and cross-border payments, transparent elections, land registry management [and] transparent crowdfunding.”
Let’s look at some of the different ways Blockchain could benefit developing economies, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa.
1. Creating financial infrastructure and accountability
According to a study by the Milken Institute, viable financial markets require consistent, accurate data on assets and credit histories. Luckily, Blockchain may fulfil these needs.
The use of Smart Contracts technology is ideal in areas lacking accountability, such as the real estate or land/agricultural sectors. In Africa, a lack of record-keeping practices often leads to “missing” or non-existent title deeds. In some cases, this is intentional.
Title deeds “go missing,” only to end up in the hands of benefactors other than the rightful owners. Smart Contracts could eradicate these issues through the use of special tokens that cannot be duplicated, changed or removed. See the article on tokenization.
Likewise, Bitland, a company in Ghana, currently helps individuals record deeds and land surveys. By resolving land disputes, Bitland creates more stability while accurately recording land asset data.
“There’s a massive number of people in the informal sector, but there’s not much data being collected on them right now.”
Merit Webster, co-president of the MIT Sloan Africa Business Club.
“That means you don’t have that credit history or payment history for them. If you have a decentralized approach to collecting data, you end up with more malleable data. [This] is very valuable for creating credit histories.”
The agricultural industry also has the potential to thrive using Blockchain.
“Blockchain could be used to track goods around the world. This allows farmers to earn a fair wage for their goods.”
Also, farmers could use record-keeping technology to streamline the supply chain and document resources. This would lead to better efficiency, lower transactional costs, and improved logistics.
2. Security in banking
According to the World Bank, there were 1.7 billion people with no bank account in 2017. This situation is worst in developing countries, especially African ones. For example, over 62 million of these people lived in Nigeria.
Besides, data from Google Trends reveal that Lagos, one of Nigeria’s biggest cities, ranks globally as the number one city based on the volume of online searches for Bitcoin (BTC). Clearly, for the city’s 21 million-odd people, there an immense interest in some form of an accessible payment system.
Of course, it’s unrealistic to expect bank branches to magically appear in every remote corner of the world. However, a digital database using Blockchain technologies has the potential to reach far beyond physical banks.
Many Africans value trust and transparency. In developing countries, this lack of trust goes beyond the Internet. Developing countries with less industrialization tend to have higher levels of corruption.
This reduces national investment opportunities in the public sector and instills a lack of trust in centralized oligarchs handling an international investment.
Because its power lies within the community of users, Blockchain can combat these trust issues. All data logs and amendments must pass through this community and identification confirmation tests.
Blockchain technology also secures your data incredibly. Hacking and data breaches are all too common nowadays. In 2017, for example, around 3 billion Yahoo user accounts were stolen.
When information is stored in the same place, hackers have one, easy target. In contrast, Blockchain is a distributed entity. This dissemination of data leaves it far less vulnerable to cyberattacks.
3. Fostering Entrepreneurship
Coupled with the Internet, Blockchain technology could be the perfect platform for aspiring African developers. Because the ‘source code’ is free of charge, skilled coders can adapt, create, and configure special applications, called DApps.
These are available on Crypto platforms and provided by companies like Ethereum, and a South African firm specializing in what they called the Keto-Coin.
Rather than waiting for governments to drag their feet trying to create jobs—individuals on the continent can form small firms that build and sell Crypto-based Apps locally or abroad.
“Despite the frictions and impediments mentioned,” said Olorunfemi. “Blockchain can still provide an avenue for promising African tech projects to access capital (FDI) via token offerings on digital assets exchanges.”
Many courses are even readily available online to quickly learn about new technology. Microsoft, for instance, offers a platform via Azure for you to build and learn about the Blockchain.
One-man shops in countries with unfavourable economic systems, like Zimbabwe, can also adopt smaller, stable, Cryptocurrencies to facilitate or payments. In cases of rampant inflation, they can temporarily act as a store of value or help you pay for things until your currency stabilizes.
As with the Venezuelan hyperinflation case study, Cryptocurrency intervention could help many developing countries troubled with economic instability.
There is also the option of Crypto-mining. But before you pull out the ‘high-consumption energy’ argument – think outside the box for a moment. What about energy sources that are free and available nearly 24/7? Like water and the sun!
The African continent is full of capable scientists and mechanical engineers. One could build special solar-powered energy centers to power Bitcoin-mining.
And without the expertise, governments or private companies could alternatively just invite Crypto companies with abundant financial resources to mine (cleanly) for a special tax/fee while creating jobs for the locals.
4. Elections
In addition to the financial side of things, Blockchain technology could help eliminate some forms of corruption. For example, many African countries’ elections are incredibly vulnerable to the social scourge. In some extreme cases, some officials change or forge written ballot votes to rig elections.
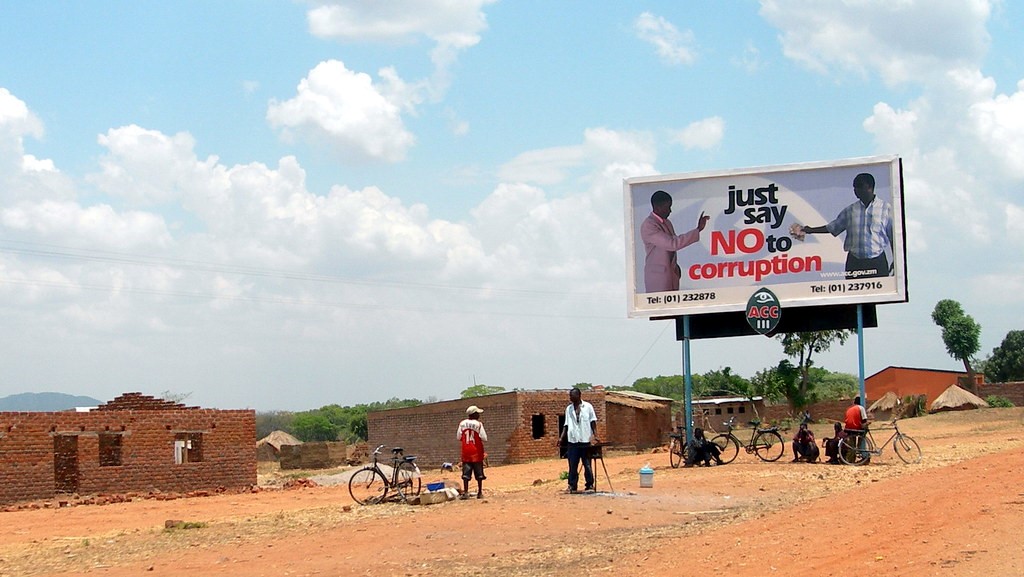

To combat this, Blockchain databases could record votes. This makes it nearly impossible to tamper with using Smart Contract technology. Having fair elections improves infrastructure, which then increases development and economic dependability.
Blockchain non-profit company Cardano, this year, has partnered with the Ethiopian government to battle these issues specifically.
5. Leapfrogging
While some might see Africa’s economy as underdeveloped, others might see it as a blank canvas well-suited for a large-scale implementation of Blockchain. Economic and governmental systems are shifting and slightly shaky in many Sub-Saharan African nations.
The challenge is to foster a rigid economic system to implement Blockchain.
Don’t just take our word for it—African nations have often implemented new, practical technologies before the Western world. Let’s look at the example of M-Pesa. Back in 2014, Americans and Europeans were amazed by Apple Pay’s launch.
However, this mobile payment system wasn’t exactly “new.” By that time, Kenyans had used M-Pesa, a very similar technology, for years.
“There’s a lot of opportunity to leapfrog the way the West developed and have these more unique African solutions, but it needs to come from within,” said Webster.
“It needs to come from entrepreneurs in the continent who want to implement these solutions. It’s important to engage people very early on. Systems incubated in the West don’t stand as great of a chance to work as African ones do.”
Concluding remarks
With the possibility of an experimental, large-scale takeover of Blockchain technology to improve African infrastructure, the nations there could leapfrog in development and growth.
This must begin internally. According to Olorunfemi, “Education—of policymakers and other stakeholders—which is often ignored has to be a critical factor in paving the way for the acceptance and adoption of new technologies and the accompanying investment.”
The results in Sub-Saharan African countries could help eliminate much of the world’s poverty. It would also remove remnants of mistrust and corruption left behind by the days of colonial exploitation.
While there are some obstacles to large-scale Blockchain implementation, we can’t think of a better benefactor than there. The possibilities for business using the Blockchain are endless!
To learn more about how to get started with Cryptocurrency mining or purchasing, visit our resources page for useful links and guides.